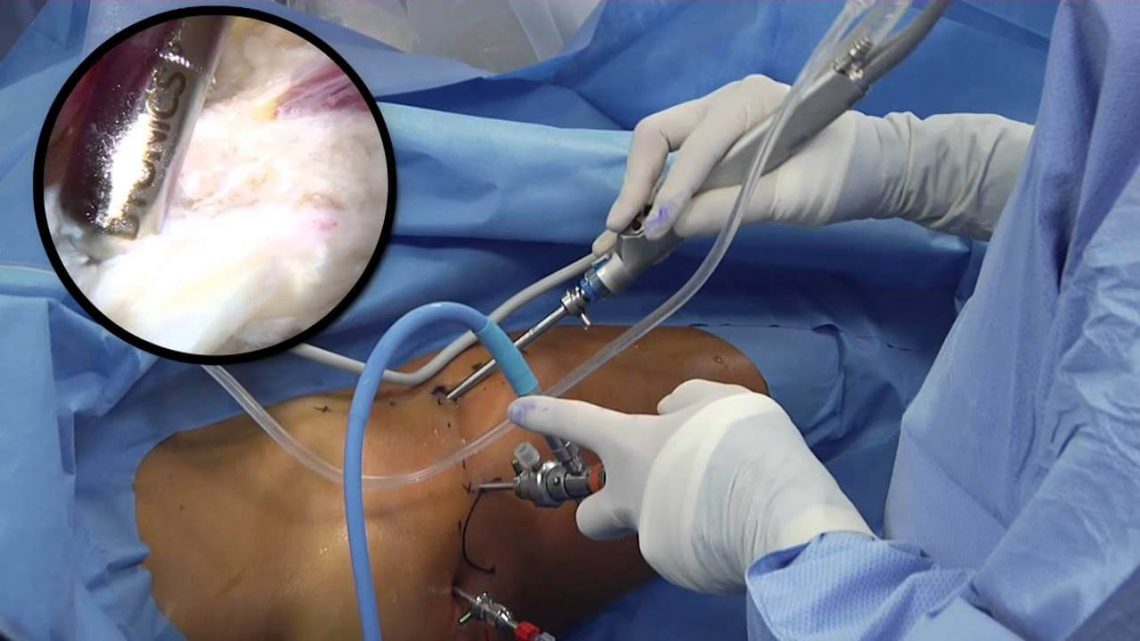
Arthroscopy is a procedure for diagnosing and treating joint problems. A surgeon inserts a narrow tube attached to a fiber-optic video camera through a small incision — about the size of a buttonhole. The view inside the joint is transmitted to a high-definition video monitor.
By attaching the arthroscope to a miniature television camera, the surgeon is able to see the interior of the joint this small incision rather than a large incision needed for surgery.
Arthroscopy is recommended if a person has inflammation in a joint, has injured a joint, or has damaged a joint over time. Patients can have arthroscopy on any joint. Most often, it’s done on the knee, shoulder, elbow, ankle, hip or wrist.
Diagnostic Procedures
Doctors often turn to arthroscopy if X-Rays and other imaging studies have left some diagnostic questions unanswered.
During the Procedure
The type of Anesthesia used varies by procedure.
- Local Anesthesia – numbing agents are injected below the skin to block sensation in a limited area, such as the knee. The patient will be awake during the arthroscopy, but the most they’ll feel is pressure or a sensation of movement within the joint.
- Regional Anesthesia – the most common form of regional anesthesia is delivered through a small needle placed between two of the spine’s lumbar vertebrae. This numbs the bottom half of the body while the patient remains awake.
- General Anesthesia – depending on the length of the operation, it may be better for the patient to be unconscious during the procedure. General anesthesia is delivered through a vein (intravenously).
After the procedure
Arthroscopic surgery usually doesn’t take long. For example, arthroscopy of the knee takes about an hour. After that, the patient will be taken to a separate room to recover for a few hours before going home.
The patient aftercare may include;
- Medications – the doctor may prescribe medication to relieve pain and inflammation.
- R.I.C.E – At home, may find it helpful to rest, ice, compress and elevate the joint for several days to reduce swelling and pain.
- Protection – patients might need to use temporary splints — slings or crutches for comfort and protection.
- Exercises – the doctor might prescribe physical therapy and rehabilitation to help strengthen the patient’s muscles and improve the function of their joint.
What We Offer
We at Almurshidi Medical Tourism will find the best doctors to cater to your needs. We are partnered with a wide network of hospitals and clinics that provide top quality medical experience.
We provide free medical estimates, make medical appointments, and provide several medical opinions if needed at no cost.
Contact Us
For more information contact us at +66822004040 or via WhatsApp