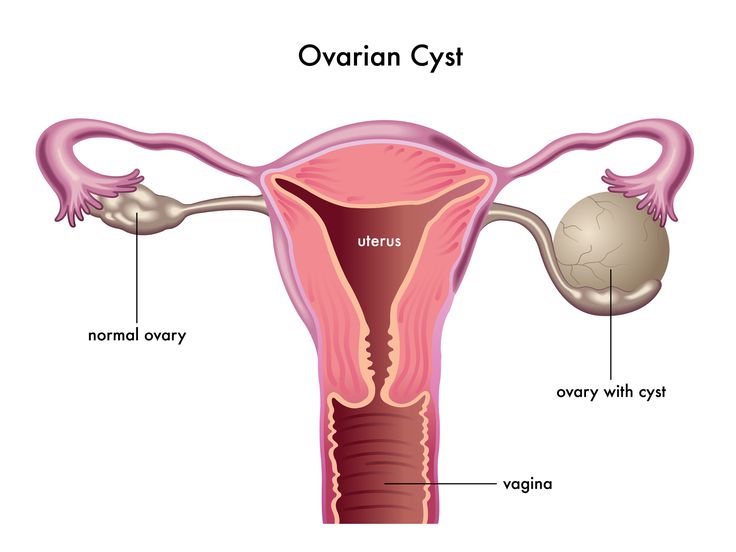
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs or pockets in an ovary or on its surface. Women have two ovaries — each about the size and shape of an almond — on each side of the uterus. Eggs (ova), which develop and mature in the ovaries, are released in monthly cycles during the childbearing years.
A cyst becomes a problem when it doesn’t go away or gets bigger. It can become painful. There’s also the possibility of cancer, but it’s rare. The changes go up as a person gets older.
Types of Ovarian Cysts
There are various types of ovarian cysts, such as dermoid cysts and endometrioma cysts. However, functional cysts are the most common type. The two types of functional cysts include follicle and corpus luteum cysts.
Follicle Cyst
During a woman’s menstrual cycle, an egg grows in a sac called a follicle. This sac is located inside the ovaries. In most cases, this follicle or sac breaks open and releases an egg. But if the follicle doesn’t break open, the fluid inside the follicle can form a cyst on the ovary.
Corpus Luteum Cysts
Follicle sacs typically dissolve after releasing an egg. But if the sac doesn’t dissolve and the opening of the follicle seals, additional fluid can develop inside the sac, and this accumulation of fluid causes a corpus luteum cyst.
Other types of Ovarian Cysts include;
- Dermoid cysts – sac-like growths on the ovaries that can contain hair, fat and other tissue
- Cystadenomas – noncancerous growths that can develop on the outer surface of the ovaries
- Endometriomas – tissues that normally grow inside the uterus can develop outside the uterus and attach to the ovaries, resulting in a cyst.
Some women develop a condition called polycystic ovary syndrome. This condition means the ovaries contain a large number of small cysts. It can cause the ovaries to enlarge. If left untreated, polycystic ovaries can cause infertility.
Symptoms
Most cysts don’t cause symptoms and go away on their own. However, a large ovarian cyst can cause:
- Pelvic pain – a dull or sharp ache in the lower abdomen on the side of the cyst
- Fullness or heaviness in the abdomen
- Bloating
When to see a doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if a person has;
- Sudden, severe abdominal or pelvic pain
- Pain with fever or vomiting
If a person has these signs and symptoms or those of shock — cold, clammy skin; rapid breathing; and lightheadedness or weakness — see a doctor right away.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the patient’s age, the type and size of their cyst, and their symptoms. The doctor might suggest;
- Watchful waiting – In many cases the patient can wait and be re-examined to see if the cyst goes away within a few months.
- Medication – the doctor might recommend hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills, to keep ovarian cysts from recurring. However, birth control pills won’t shrink an existing cyst.
- Surgery – the doctor might suggest removing a cyst that is large, doesn’t look like a functional cyst, is growing, continues through two or three menstrual cycles, or causes pain.Some cysts can be removed without removing the ovary (ovarian cystectomy). In some cases, the doctor might suggest removing the affected ovary and leaving the other intact (oophorectomy).
What We Offer
We at Almurshidi Medical Tourism will find the best doctors to cater to your needs. We are partnered with a wide network of hospitals and clinics that provide top quality medical experience.
We provide free medical estimates, make medical appointments, and provide several medical opinions if needed at no cost.
Contact Us
For more information contact us at +66822004040 or via WhatsApp





