
A diagnosis of infertility means a person is not able to get pregnant after a year of trying. If they are a woman over 35, it means they haven’t been able to get pregnant after 6 month of trying. Women who are able to conceive but not carry a pregnancy in term may also be…
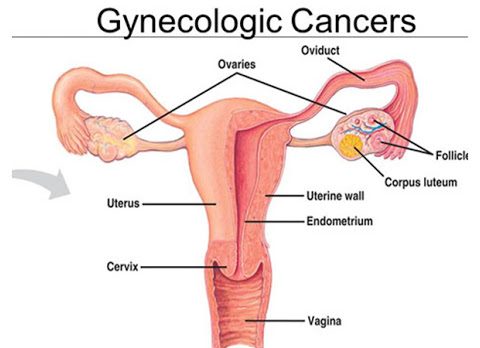
Types of Gynecological Cancer Gynecological cancers are those that develop in a woman’s reproductive tract. Cervical cancer is only one type of gynecological cancer. Other types include; Cervical cancer – vast majority of cases of cervical cancer are linked to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. The majority of women with an HPV infection will not develop…
Diphtheria is a serious bacterial infection that usually affects the mucous membranes of the nose and throat. Diphtheria can be treated with medication. But in advanced stages, diphtheria can damage the heart, kidneys and nervous system. Even with treatment, diphtheria can be deadly, especially in children. Symptoms Signs of diphtheria often appear within two to…
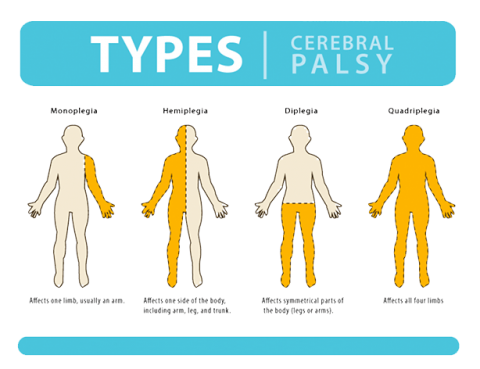
Cerebral palsy (CP) refers to a group of disorders that affect muscle movement and coordination. In many cases, vision, hearing, and sensation are also affected. Cerebral means having to do with the brain. Palsy means weakness or problems with using the muscles. CP is caused by abnormal brain development or damage to the developing brain…
People may be affected by many different types of blood conditions and blood cancers. Common blood disorders include anemia, bleeding disorders such as hemophilia, blood clots, and blood cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma. Blood disorders can affect any of the three main components of blood; Red blood cells, which carry oxygen to the…
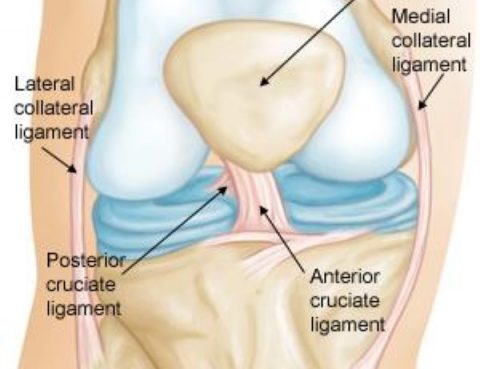
Ligament injuries in the knee — such as an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) — can put a person on the sidelines — fast. They hurt a lot and may limit what a person can do. What is Ligament? Ligaments are small bands of tough, flexible tissue, made up of lots of individual fibres, which connect…
Vascular dementia is a type of dementia that accounts for around 20% of diagnoses, roughly 150,000 people. It is caused by reduced blood flow to the brain and is most common in those aged over 65. Vascular dementia can be developed after a stroke blocks an artery in the brain, but strokes don’t always cause…

Cancer screening tests aim to find cancer early, before it causes symptoms and when it may be easier to treat successfully. Effective screening tests are those that; Find cancer early Reduce the chance that someone who is screened regularly will die from cancer Have more potential benefits than harms. Getting screening tests regularly may find…
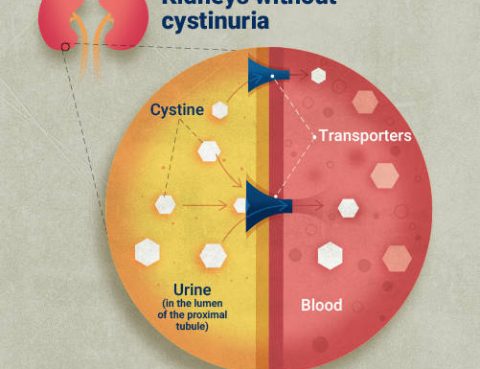
Cystinuria is an inherited disease that causes stones made of the amino acid cystine to form in the kidneys, bladder, and ureters. Inherited diseases are passed down from parents to children through a defect in their genes. To get cystinuria, a person must inherit the defect from both parents. Symptoms Cystinuria is usually asymptomatic when…
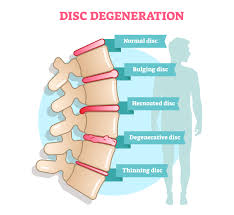
Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is an age-related condition that happens when one or more of the discs between the vertebrae of the spinal column deteriorates or breaks down, leading to pain. The discs in a person’s back are located in between the vertebrae of the spine. They act as cushions and shock absorbers. Discs help…
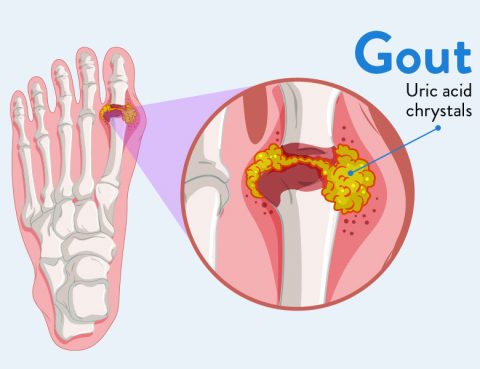
Gout is a form of arthritis caused by excess uric acid in the joints. It is a common and complex form of arthritis that can affect anyone. It’s characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, swelling, redness and tenderness in the joints, often the joint at the base of the big toe. Symptoms of Gout…
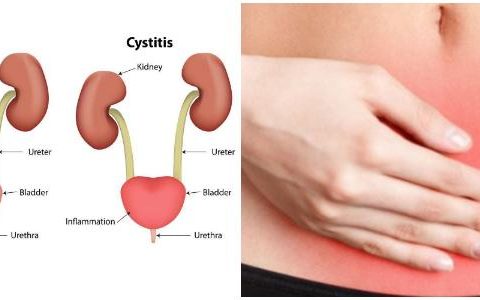
A bladder infection is most often caused by a bacterial infection within the bladder. For people with weakened immune systems, yeast can cause bladder infections as well. A bladder infection is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI). This refers to an infection anywhere in the urinary tract, such as the bladder, kidneys, ureters, or…
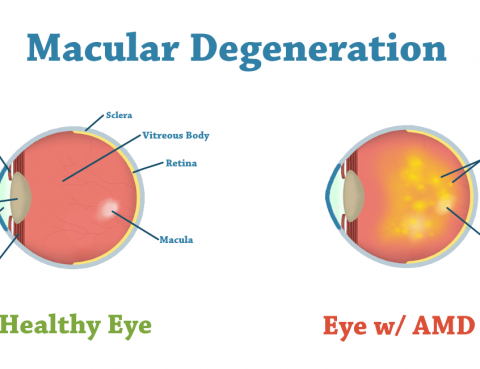
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is an eye disease that may get worse over time. It’s the leading cause of severe, permanent vision loss in people over the age of 60. It happens when the small central portion of the retina, called macula, wears down. The retina is the light sensing nerve tissue at the back…
Bowel incontinence is the inability to control bowel movements that results in involuntary bowel movements (fecal elimination). This can range from an infrequent involuntary passage of small amounts of stool to a total loss of bowel control. It’s a common problem, especially among older adults. Accidental bowel leakage is usually not a serious medical problem….
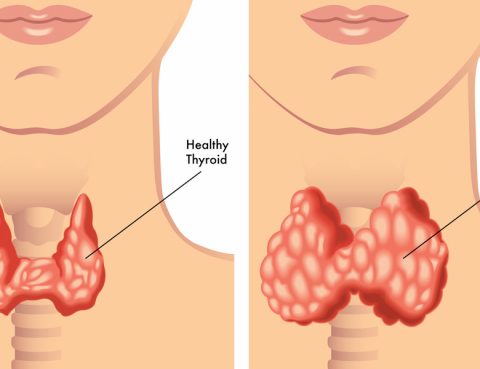
Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) is a condition in which the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough of certain crucial hormones. Hypothyroidism may not cause noticeable symptoms in the early stages. Over time, untreated hypothyroidism can cause a number of health problems, such as obesity, joint pain, infertility and heart disease. Symptoms The most common signs and symptoms…
High cholesterol or Hyperlipidemia is a common problem. The term covers several disorders that result in extra fats, also known as lipids, in the blood. Some of its causes can be controlled, but not all of them. The two major types of lipids (fats) found in the blood are triglycerides and cholesterol. Triglycerides are made…

Almurshidi Medical Tourism Agency always welcomes you to receive the medical services in our hospital. However, to travel to Thailand, you must apply for the certificate of entry from the Royal Thai embassy in your country of residence. The patient and attendant (s) must be quarantined for 14 days upon arrival to comply with the…
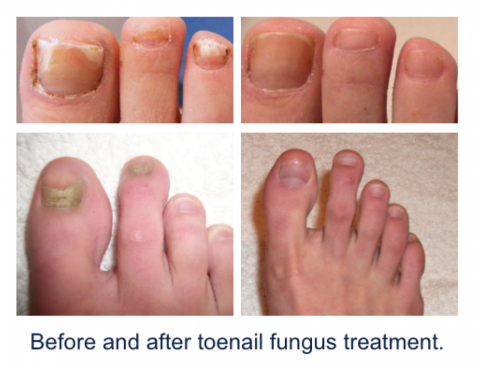
Fungus infections can affect any part of the body. Fungi are normally present in and on the body alongside various bacteria. But when the fungus begins to overgrow, the person can get an infection. Nail fungus is a common condition that begins as a white or yellow spot under the tip of the fingernail or…

Malaise is described as any of the following; A feeling of overall weaknessA feeling of discomfortA feeling like having an illnessSimply not feeling well It often occurs with fatigue and an inability to restore a feeling of health through proper rest. Depending on the cause, malaise can start slowly or hit suddenly. Scores of illnesses…

Refractive errors are a type of vision problem that makes it hard to see clearly. They happen when the shape of the eye keeps light from focusing correctly on the retina (a light-sensitive layer of tissue in the back of the eye). The most common types of refractive error are; Near-sightedness – results in far…
