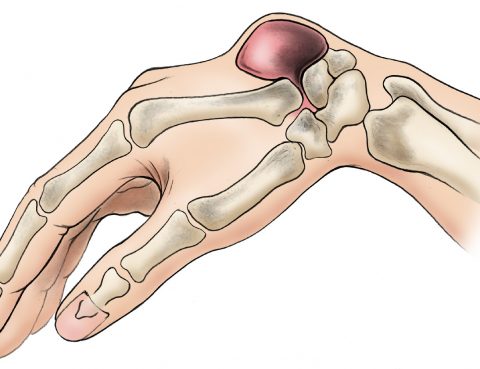
A ganglion cyst is a small sac of fluid that forms over a joint or tendon (tissue that connects muscle to bone). Inside the cyst is a thick, sticky clear, colorless, jellylike material. Depending on the size, cysts may feel firm or spongy. Small ganglion cyst can be pea-sized, while larger ones can be around…
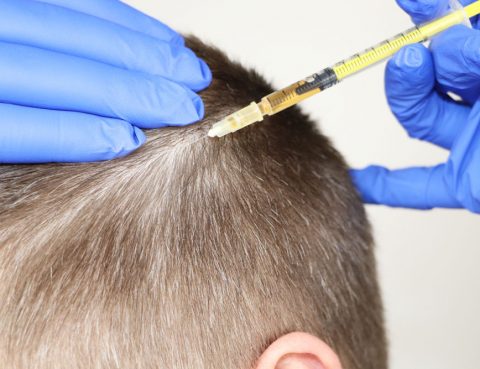
Hair loss is currently one of the most common problems. Though losing 25 to 50 hair strands in a day is normal, sometimes, the hair loss can be a lot more and rapid, causing worry and concern. Mesotherapy may help prevent hair loss, improve hair quality , and stimulate hair growth. Hair mesotherapy is also…
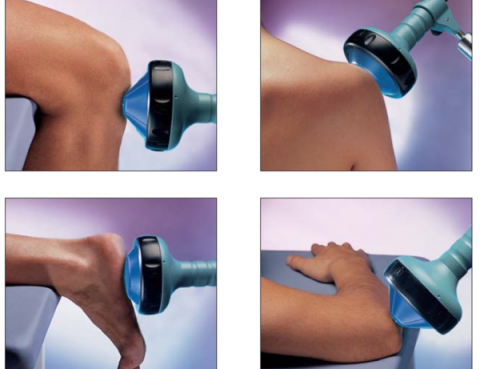
Shockwave therapy is a multidisciplinary device used in orthopaedics, physiotherapy, sports medicine and urology. It is a treatment method in which an applicator is used to direct radial “shockwaves” on the part of the body that needs to be treated. What is it applicable for? Shockwave therapy is a treatment used for a wide variety…

Hyperhidrosis is abnormal excessive sweating that’s not necessarily related to heat or exercise. A person may sweat so much that it soaks through their clothes or drips off their hands. Besides disrupting normal daily activities, this type of sweating can cause social anxiety and embarrassment. Excessive sweating from the underarms or of the palms and…
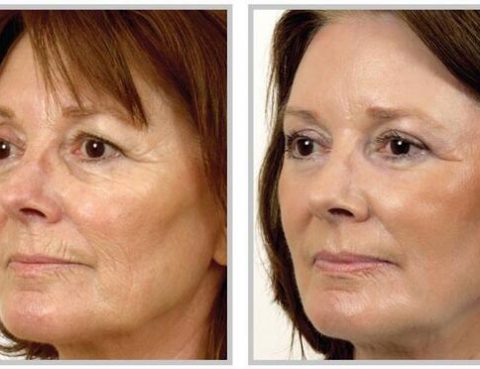
The thermalift procedure is an advanced way of tightening skin without surgery. It is also known as thermoplastic contouring or ThermaCool, it is non-invasive and there is no “downtime” or recuperation required. The treatment uses a radiofrequency device to stimulate the production of collagen and elastin by delivering heat to cells in the lower layers…

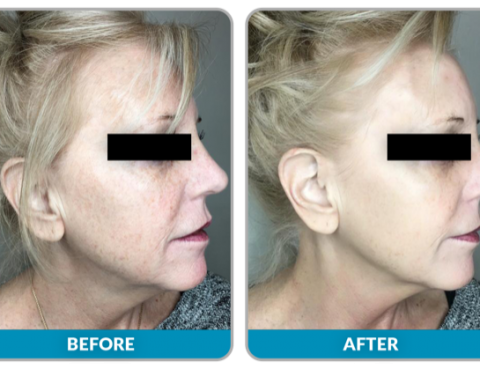
Otoplasty also known as cosmetic ear surgery is a procedure to change the shape, position or size of the ears. A defect in the ear structure that is present at birth or that becomes apparent with development can be corrected by otoplasty. This procedure can also treat misshapen ears caused by injury. Otoplasty creates a…
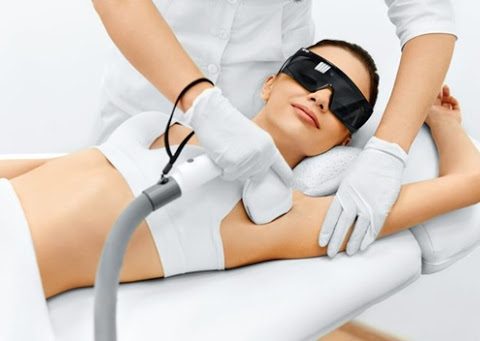
Laser hair removal is one of the most commonly done cosmetic procedures. It beams highly concentrated light into hair follicles. Pigment in the follicles absorb light. That destroys hair. It uses the concentrated beam of light (laser) to remove unwanted hair. It is a long-lasting form of hair removal that damages or destroys the hair…
The jet peel facial is a non-invasive dermal fusion system that delivers immediate visible results without downtime or skin irritation. The jet peel combines oxygen and a liquid such as water, anesthetic or skin nutrients to create a jet stream of micro-droplets that penetrates deep into the skin. It is ideal for all skin types,…

Intragastric balloon placement is a weight-loss procedure that involves placing a saline-filled silicone balloon into a person’s stomach. This helps in losing weight by limiting how much a person can eat and making them full faster. It is the latest weight loss procedure. A soft, round, inflatable balloon made of medical-grade silicon is placed inside…

Bipolar disorder, formerly called manic depression, is a mental health condition that causes extreme mood swings that include emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and low (depression). People with bipolar disorder have periods or episode of: Depression – feeling very low and lethargic Mania – feeling very high and overactive (less severe mania is known as hypomania)…
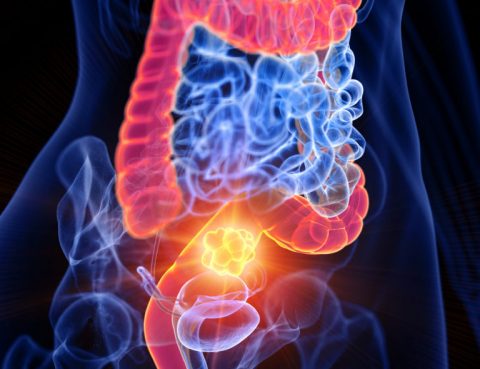
The colon is the large intestine (bowel) and the rectum is the end of the bowel where stools are stored. Ulcerative colitis is a long-term condition where the colon and rectum become inflamed. This inflammation produces tiny sores called ulcers on the lining of the colon. It usually begins in the rectum and spreads upwards….
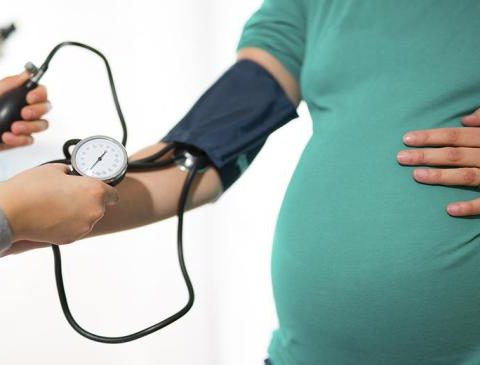
Pre-existing conditions can worsen during pregnancy, threatening the health of a mother and her child. Asthma, diabetes, and depression can harm the mother and child during pregnancy if not managed properly. Pregnancy can cause a healthy mother’s red blood cell count to drop, a condition called anemia, or induce depression. Another problem arises when a…

Down syndrome also known as trisomy 21, is a condition in which a person has an extra chromosome. It is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. In every cell in the human body there is a nucleus, where genetic material is stored in…
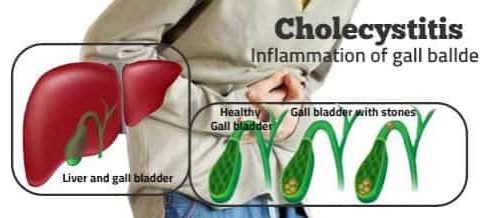
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of the abdomen, beneath the liver. The gallbladder holds a digestive fluid that’s released into the small intestine. Cause Gallstones are by far the most common cause of acute cholecystitis. Bile can build up in the gallbladder if…
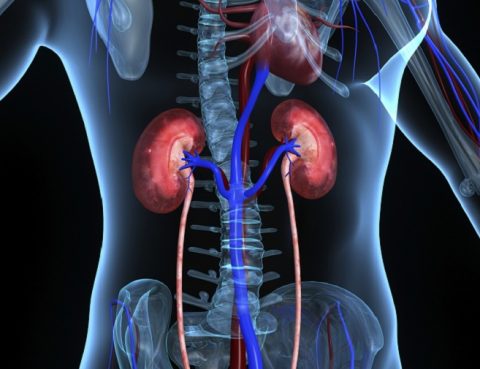
Kidney stones can develop in one or both kidneys and most often affect people aged 30 to 60. It is quite common, with around three in 20 men and up to two in 20 women developing them at some stage of their lives. The medical term for kidney stones in nephrolithiasis, and if they cause…
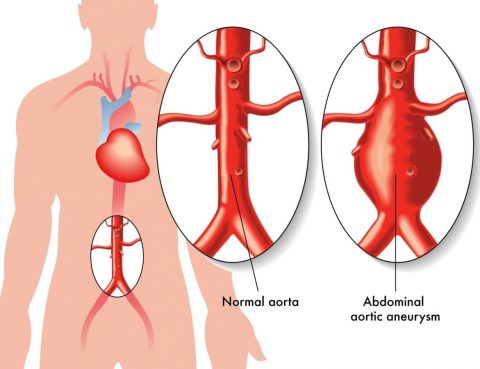
The aorta is the largest blood vessel in the human body. It carries blood from the heart up to the head and arms and down to the abdomen, legs, and pelvis. The walls of the aorta can swell or bulge out like a small balloon if they become weak. This is called an abdominal aortic…
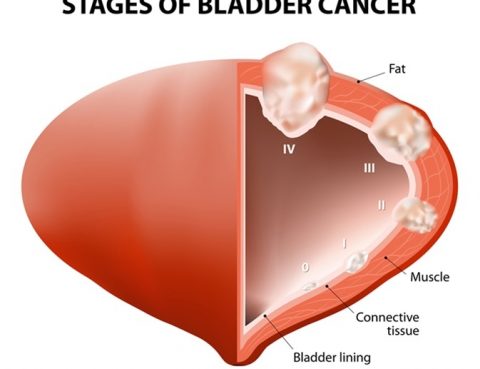
Bladder cancer is one of the most common cancers. It occurs more frequently in men than it does in women and usually affects older adults, though it can happen at any age. Bladder cancer most often begins in the cells (urothelial cells) that line the inside of the bladder — the hollow, muscular organ in…
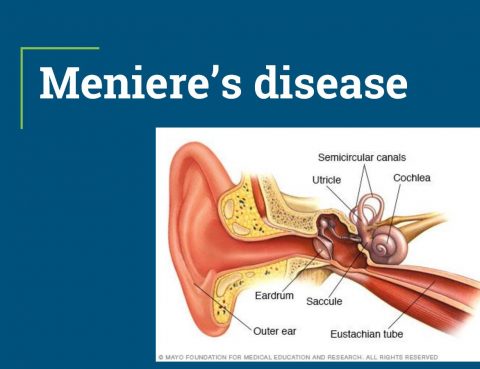
Meniere’s disease is a disorder that affects the inner ear. The inner ear is responsible for hearing and balance. The condition causes vertigo, the sensation of spinning. It also leads to hearing problems and a ringing sound in the ear. Meniere’s disease usually affects only one ear. Symptoms Recurring episodes of vertigoHearing lossRinging in the…
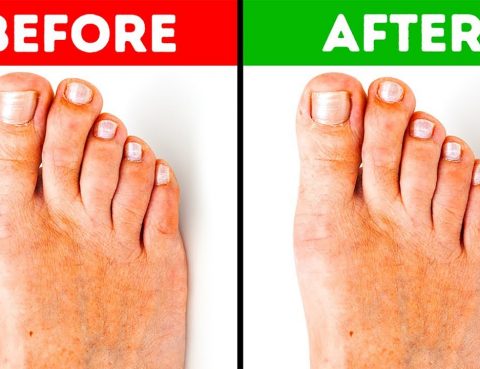
A bunion is a bony bump that forms on the joint at the base of the big toe. It occurs when some of the bones in the front part of the foot move out of place. This causes the tip of the big toe to get pulled toward the smaller toes and forces the joint…
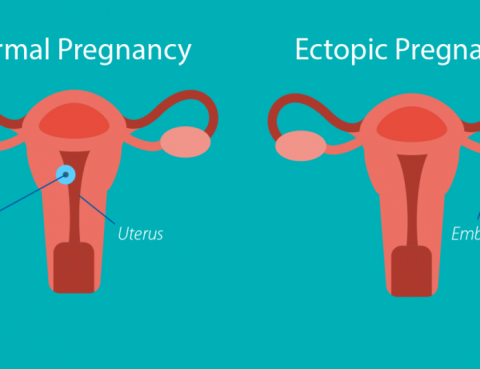
Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Pregnancy begins with a fertilized egg. Normally, the fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus. An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the main cavity of the uterus. Oftentimes ectopic pregnancy occurs in…
