
✅ Hollywood Smile: Shine with Confidence — with Almurshidi Medical Tourism A Hollywood Smile is a popular cosmetic dental procedure designed to enhance the appearance of your teeth and give you a bright, attractive smile. At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we offer this service using the latest technology and expert care. What is a Hollywood Smile?…
👁️ Eye Health: Clear Vision for a Better Life Maintaining good eye health is essential for clear vision and enjoying daily life. At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we offer advanced treatments for eye conditions using state-of-the-art medical technologies to ensure better vision and patient comfort. 🔹 The Importance of Eye Health: The eyes are sensitive and…

Your Life Matters – Get Expert Heart Treatment with Almurshidi Medical Tourism Heart conditions such as blocked arteries or heart muscle weakness require timely and accurate treatment to protect your health and save lives.At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we connect you with the top hospitals specializing in heart surgeries and catheterization in the UAE, Europe, and…

Regain Your Comfort and Mobility with Advanced Orthopedic Treatments Knee, back, or shoulder pain can seriously affect your daily life and limit your freedom of movement.At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we offer advanced and effective treatments for bone and joint pain using modern medical technologies that ensure better mobility and long-term relief. Causes and Treatments of…
Corneal Transplant: Your Way to Clearer VisionAt Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we provide advanced corneal transplant services using the latest medical techniques, guided by top ophthalmologists, to help restore your vision and enhance your quality of life. What is a Corneal Transplant? A corneal transplant is a surgical procedure where a damaged or diseased cornea is…
Foot Health: Step into Comfort and Confidence Foot health is essential for maintaining an active and pain-free lifestyle. Discomfort or issues with the feet can severely limit mobility and affect daily routines.At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we offer advanced solutions for treating foot-related conditions in partnership with top podiatrists and orthopedic specialists, using modern medical technologies…
🔹 Digestive Problems: Toward Better Health Digestive system issues are common conditions that can affect your daily life, causing symptoms like pain, bloating, or difficulty in digestion.At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we provide advanced medical services to treat digestive problems using the latest technologies to ensure better health and comfort for our patients. 🩺 Causes and…

Stem Cells: The Future of Advanced Medical Treatment Stem cells are among the most promising breakthroughs in modern medicine. These unspecialized cells can develop into various specialized cell types in the body, making them a powerful tool in treating many chronic and complex conditions. At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we provide expert information and services related…
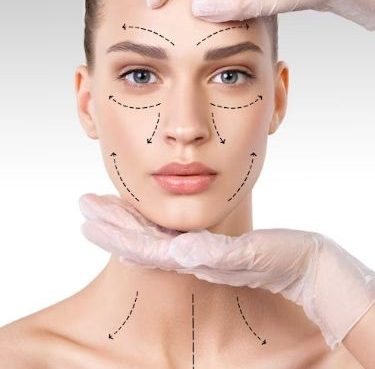
Facelift and Neck Lift: Toward a Younger and More Confident Look Facelift and neck lift procedures help rejuvenate the skin and reduce visible signs of aging by tightening and improving overall appearance. At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we offer advanced solutions using the latest medical technologies to ensure natural and safe results. What Is a Facelift…
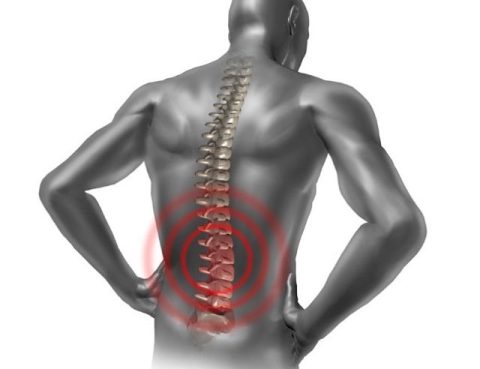
Back Pain: Towards Comfort and Better Mobility Back pain is one of the most common health issues worldwide, often affecting your daily activities, work productivity, and overall quality of life. At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we are committed to providing advanced and comprehensive back pain treatments to help you regain comfort and mobility. ✅ Common Causes…
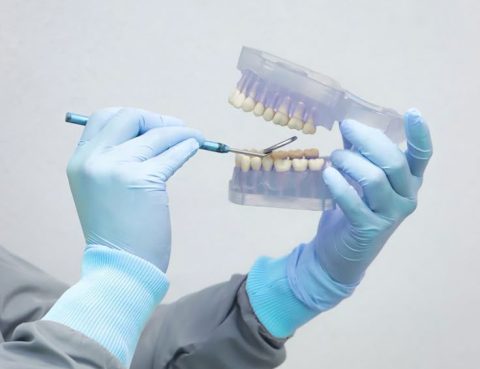
📍 Dental Implants: Restore Your Smile and Function with Almurshidi Dental implants are a highly effective solution to replace missing teeth and restore both the smile and full oral function. At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we provide advanced dental implant services using the latest medical technologies to ensure precise and comfortable results for our patients. What…
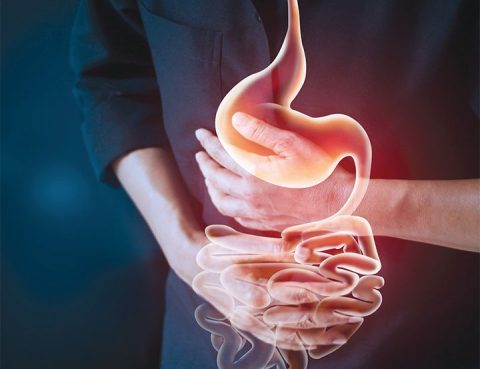
Stomach Pain Treatment: Towards Better Health Stomach pain is a common issue that can affect your daily life. At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we offer advanced treatment services for stomach pain using modern medical techniques to ensure better health and patient comfort. Causes and Treatment of Stomach Pain: Stomach pain may be caused by: Ulcers Gastritis…

🧘♂️ Back Pain Treatment: Toward Better Comfort and Mobility Back pain is a common health issue that can significantly impact your daily life.At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we provide specialized back pain treatment services using advanced medical technologies to ensure comfort and improve mobility. 🔍 Causes and Treatment of Back Pain Back pain may result from:…

🚗 Luxury Transportation Service by Almurshidi Medical Tourism Patient comfort starts at the doorstep… and continues through recovery. At Al Murshidi Medical Tourism, we believe that a patient’s comfort should begin long before arriving at the hospital. That’s why we offer a luxury, private medical transportation service, tailored to provide the highest levels of comfort,…

Rheumatoid Arthritis: Understanding the Disease & Treatment Options Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and stiffness. It can impact multiple joints and hinder daily activities and mobility if left untreated. 🔹 Common Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Joint pain and swelling Morning stiffness Fatigue and exhaustion Limited…
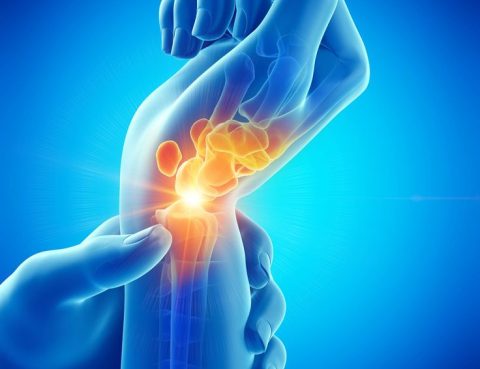
🔹 Wrist Joint Treatment: Regain Movement and Comfort Are you experiencing pain or limited mobility in your wrist joint that’s affecting your daily life?At Almurshidi for Medical Tourism, we offer advanced treatments for wrist joint problems using cutting-edge techniques, in collaboration with top orthopedic specialists. 🦴 What is the Wrist Joint? The wrist joint is…
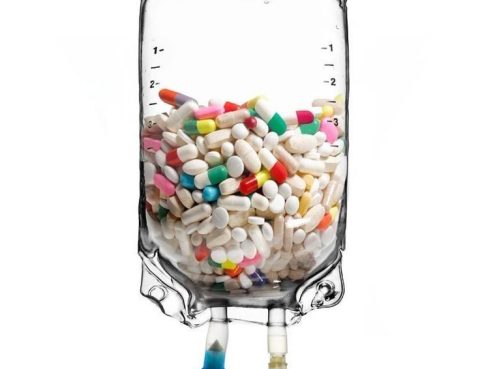
IV Vitamins – Boost Your Health and Energy Looking for a safe and effective way to enhance your health and energy levels?At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we offer advanced IV vitamin therapy administered by expert medical professionals using the latest technology. What is IV Vitamin Therapy?IV vitamins are treatments delivered directly into the bloodstream, allowing your…
Body Whitening: Enhance Beauty and Confidence Looking for ways to improve your skin’s appearance and achieve full body whitening? At ALmurshidi Medical Tourism, we offer advanced and safe body whitening treatments. These procedures can help enhance skin beauty and boost your self-confidence. What is Body Whitening? Body whitening is a cosmetic procedure aimed at lightening…
🌟 Dental Treatment: For a Healthy and Beautiful Smile | Almurshidi Medical Tourism Are you looking for dental treatment to achieve a healthy and beautiful smile? At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we offer professional dental care services using advanced medical techniques to help you improve your oral health and restore your smile with confidence. 🔹 What…

📝 Gender Selection in Georgia – An Advanced Option to Fulfill Your Dream Are you looking for a way to choose the gender of your future baby? At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we offer comprehensive gender selection services in Georgia, using the latest medical technologies and in cooperation with top fertility specialists. Georgia is becoming one…
