
🌍 Travel for Treatment with Ease — Choose Almurshidi Medical Tourism In a world where medical travel has become more convenient than ever, Almurshidi Medical Tourism stands out as the perfect choice for anyone seeking trusted medical care and complete comfort during their medical or cosmetic journey. With Almurshidi, you can book your medical or…

🌿 After Forty… Your Health Is a Trust! Regular medical checkups can truly save your life — before it’s too late ✅ Once we reach our forties, our bodies begin to send us subtle signs that we may easily overlook. However, these signals often carry important warnings about our health. That’s why having regular checkups…

After the age of forty… your health is a trust! Regular checkups can save your life before it’s too late ✅ As we enter our forties, our bodies begin to send subtle signals that we may not easily notice — yet these signals can carry important warnings about our health. This is why regular medical…

Toothache: When Should You Seek Treatment?Are you experiencing tooth pain? At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we understand the importance of dental health and the need for prompt treatment when discomfort arises. 🔹 Common Causes of Tooth Pain: Tooth decay: Can cause intense pain if left untreated. Gum disease: Leads to discomfort and pain in the gums…
📌 India Electronic Arrival Card: Complete Guide The Government of India has introduced the Electronic Arrival Card system for all non-Indian travelers, aiming to streamline the entry process and enhance immigration efficiency. ✅ What is the Electronic Arrival Card? The Electronic Arrival Card is a digital document that non-Indian travelers must fill out prior to…

Eye Examination in Thailand: High-Quality Care at Affordable Prices Thailand is not only a top tourist destination, but also home to some of the best medical centers offering comprehensive eye exams at affordable prices. ✅ Why Choose an Eye Exam in Thailand? Affordable Prices: Eye check-up costs are lower than in many other countries. Excellent…

Comprehensive Vitamin Test – Discover What Your Body Needs with Almurshidi Feeling tired or fatigued without a clear reason?It could be due to a deficiency in essential vitamins and nutrients. Book your Comprehensive Vitamin Test now with Almurshidi to identify what your body needs and regain your energy and health. 💡 The test helps…

💆♂️ Physical Therapy: Relaxation and Healing for Your Body — with Almurshidi Physical therapy is a natural treatment method that uses techniques like massage, hydrotherapy, and therapeutic exercises to improve health and well-being. It can help relieve pain, restore mobility, and enhance flexibility. ✅ Benefits of Physical Therapy: Relaxation and comfort: Reduces stress and anxiety,…

✅ Colon Cleansing: A Fresh Start for Your Digestive Health – Almurshidi Colon cleansing is a medical procedure designed to flush out toxins and waste buildup from the colon, helping improve digestive health and promote overall well-being. If you suffer from bloating, chronic constipation, or digestive discomfort, colon cleansing might be the right solution for…

Flight Deals from Fujairah to Bangkok – Almushidi Planning a trip to Bangkok? Discover the best flight deals from Fujairah to Bangkok with Almushidi! Affordable prices and flexible options for every traveler. Book now and experience the magic of Thailand. 🔹 Top Travel Offers: Direct Flights: Fly nonstop with top airlines like Thai Lion Air…

Migraine: Causes and Treatment Migraines can be a bothersome and life-disrupting condition.At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we offer advanced migraine treatment services using the latest medical technologies to ensure patient comfort and care. 🧠 Common Causes of Migraine: Stress and emotional pressure – major triggers for migraines. Hormonal changes – especially in women, can lead to…
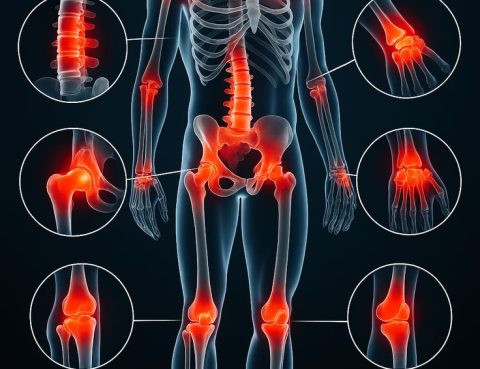
Bone & Joint Pain: Causes and Treatment At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we understand how bone and joint pain can disrupt your daily life. That’s why we provide world-class solutions and access to top specialists using the latest medical technologies. 🔹 Common Causes of Bone and Joint Pain: Arthritis (e.g. osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis) Muscle or ligament…

💧 Excessive Sweating (Hyperhidrosis): Causes & Treatment – with Almurshidi for Medical Tourism Hyperhidrosis is a medical condition where the body produces excessive sweat beyond what is necessary, often causing discomfort and embarrassment.At Almurshidi for Medical Tourism, we provide cutting-edge treatments to help you manage and overcome this condition with confidence. 🔍 What Causes Hyperhidrosis?…

Weight Loss: Causes and Treatment Unintentional or unhealthy weight loss can be a serious medical concern. At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we provide advanced treatment solutions using the latest medical technologies to help patients regain healthy weight safely and effectively. 🔍 Causes of Weight Loss: Chronic Diseases: Such as diabetes or thyroid disorders. Poor Nutrition: An…

Hair Loss: Causes and Treatment Hair loss can be a frustrating issue and can greatly affect one’s appearance. At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we offer advanced hair loss treatment services using the latest medical technologies to ensure excellent results and patient comfort. Causes of Hair Loss: Genetics: Hair loss can be hereditary. Hormonal changes: Such as…
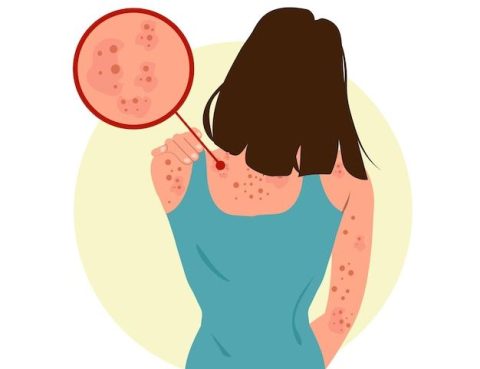
Skin Allergy: Causes and Treatment Skin allergy is a common condition that can cause itching, redness, and irritation.At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we provide advanced skin allergy treatments using the latest medical technologies to ensure the comfort and well-being of our patients. Causes of Skin Allergy: Direct contact: With irritants such as chemicals or certain plants….

✨ Full Body Check-Up with Almurshidi Medical Tourism: Peace of Mind Starts Here 💚 In a world full of stress and challenges, we often neglect our health and delay doctor visits until symptoms appear. But what if we told you there’s a simple, effective way to stay on top of your health before any issues…
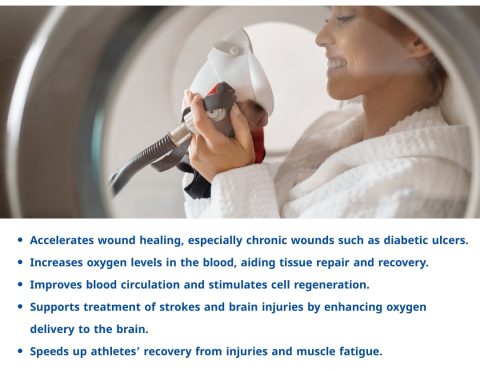
Breathe New Life with Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy SessionsLooking for a safe and natural way to improve your overall health and energy levels?Almurshidi Medical Tourism offers state-of-the-art Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) sessions, designed to support healing and enhance your well-being — all under the care of expert medical professionals. ✅ Benefits of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Wound…
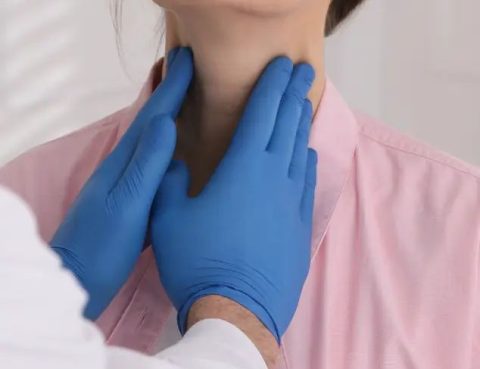
Thyroid Treatment: Restoring Hormonal Balance The thyroid gland is a vital part of the body, playing a key role in regulating metabolism and hormonal balance. If you are experiencing thyroid issues, Almurshidi Medical Tourism offers advanced medical solutions to ensure effective results and patient comfort. 🔹 Why Thyroid Treatment Matters: Restore hormonal balance: Through treatment…

Knee Pain: Causes and Treatment Knee pain can significantly affect your daily life and limit your freedom of movement. At Almurshidi Medical Tourism, we provide advanced knee pain treatments using the latest medical technologies to ensure better mobility and comfort for our patients. Causes of Knee Pain: Injuries: Such as muscle tears or fractures. Medical…
