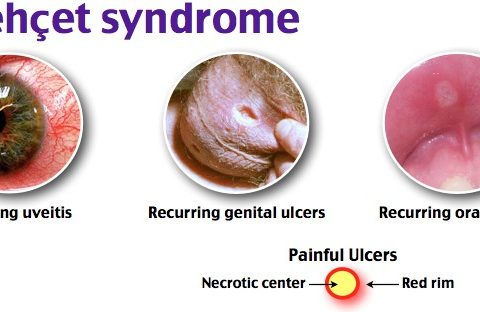
Behcet’s disease, also called Behcet’s syndrome, is a rare disorder that causes blood vessel inflammation throughout the body. The disease can lead to numerous signs and symptoms that can seem unrelated at first. They can include mouth sores, eye inflammation, skin rashes and lesions, and genital sores. Behcet’s disease is a chronic condition. The severity…
Blood poisoning is a serious infection. It occurs when bacteria are in the bloodstream. Despite its name, the infection has nothing to do with poison. Although not a medical term, “blood poisoning” is used to describe bacteremia, septicemia, or sepsis. Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening medical condition that’s associated with an infection. It is a…

Progeria, also known as Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS), is a rare genetic condition that causes a child’s body to age fast. Most kids with progeria do not live past age 13. The disease affects both sexes and all races equally. It affects about 1 in every 4 million births worldwide. Children with progeria generally appear…

Febrile seizures usually occur in young children who are between the ages of 3 months to 3 years. They’re convulsions a child can have during a very high fever that’s usually over 102.2 to 104°F (39 to 40°C) or higher. This fever will happen rapidly. The rapid change in temperature is more of a factor…

Niemann-Pick is a rare, inherited disease that affects the body’s ability to metabolize fat (cholesterol and lipids) within cells. These cells malfunction and over time die. People with niemann-pick disease have an abnormal lipid metabolism that causes a buildup of harmful amounts of lipid in various organs. The disease primarily affects the following; LiverSpleenBrainBone marrow…

Tarlov cysts are fluid-filled nerve root cysts found most commonly at the sacral level of the spine — the vertebrae at the base of the spine. These cysts typically occur along the posterior nerve roots. Cysts can be valved or non valved. These cysts are sometimes called perineural, meaning the cyst can surround (peri) a…
Dysphagia or difficulty swallowing means it takes time and effort to move food or liquid from the patient’s mouth to their stomach. Dysphagia may also be associated with pain. In some cases, swallowing may be impossible. Although the medical term “dysphagia” is often regarded as a symptom or sign, it is sometimes used to describe…

Medical Tourism Medical tourism, which is also called medical trip, means visiting abroad countries for medical services. Usually, these trips are combined with a vacation. The concept of medical tourism is not new. In the 4th century BC, Epidaurus was a center of praying and treatment for those visiting Anatolia all around the Mediterranean sea…

Desmoid tumors are noncancerous growths that occur in the connective tissues, it rarely spreads to other parts of the body. It most often occurs in the abdomen, arms and legs. Another term for Desmoid tumors is aggressive fibromatosis. The tumor may also be called one of the following; Aggressive fibromatosisDeep fibromatosisDesmoid fibromatosisFamilial infiltrative fibromatosisHereditary desmoid…
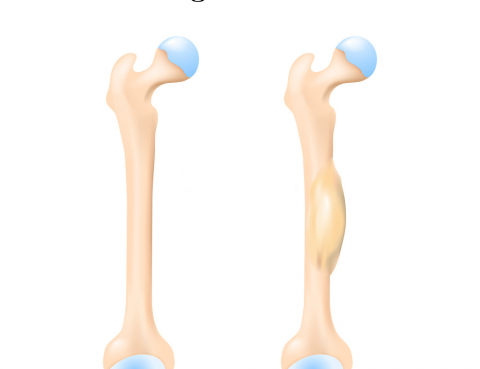
Ewing sarcoma is a rare type of cancer that occurs in bones or in the soft tissue around the bones. Ewing sarcoma most often begins in the leg bones and in the pelvis, but it can occur in any bone. Less often, it starts in the softest tissues of the chest, abdomen, limbs or other…

Asbestosis is a chronic lung disease caused by inhaling asbestos fibers. Prolonged exposure to these fibers can cause lung tissue scarring and shortness of breath. Asbestosis symptoms can range from mild to severe, and usually don’t appear until many years after continued exposure. Signs and Symptoms The signs and symptoms of asbestosis typically manifest after…

Addison’s disease, also called adrenal insufficiency, is a long-term endocrine disorder in which the adrenal glands — which sit on top of the kidneys — do not produce enough steroid hormones cortisol and aldosterone. Cortisol helps the body respond to stress, including the stress of illness, injury or surgery. It also helps maintain blood pressure,…
Septic shock is a severe and potentially fatal condition that occurs when sepsis leads to life-threatening low blood pressure. Sepsis develops when the body has an overwhelming response to infection. It occurs when the body’s response to these chemicals is out of balance, triggering changes that can damage multiple organ systems. If sepsis progresses to…
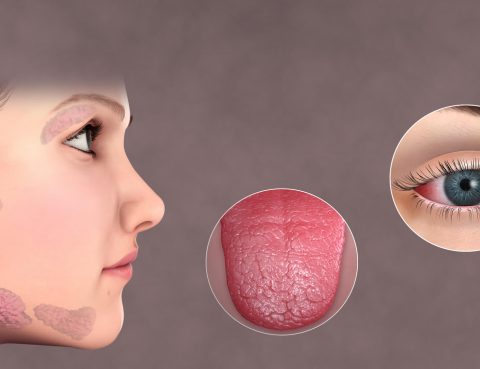
Sjogren’s syndrome is a disorder of the immune system identified by its two most common symptoms — dry eyes and a dry mouth. The condition often accompanies other immune system disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. In Sjogren’s syndrome, the mucous membranes and moisture-secreting glands of the eyes and mouth are usually affected first…

Pleurisy is a condition in which pleura — two large, thin layers of tissue that separates the lungs from the chest wall — becomes inflamed. Also called pleuritis, pleurisy causes sharp chest pain (pleuritic pain) that worsens during breathing. When a person is healthy, they will not notice the pleura at work. But if the…

Penta X Syndrome is a chromosomal abnormality in which a female has five X chromosomes instead of the normal two. The condition is due to problems during the formation of the reproductive cells in a person’s parents. Risk factors include older parents at the time of conception. Diagnosis is suspected based on symptoms and confirmed…

Heart disease is a term covering any disorder of the heart. Diseases under the heart disease umbrella include blood vessel diseases, such as coronary artery disease, heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias); and heart defects a person is born with (congenital heart defects), among others. Unlike cardiovascular disease, which describes problems with the blood vessels and circulatory…
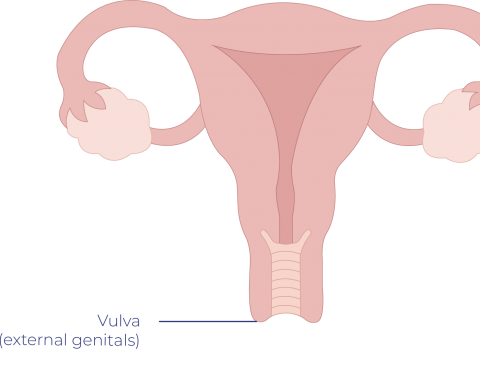
Cancer of the vulval (also called vulvar cancer or vulval cancer) is a type of cancer that occurs on the outer surface area of the female genitalia. The vulva is the area of the skin that surrounds the urethra and vagina, including the clitoris and labia. Vulvar cancer commonly forms as a lump or sore…
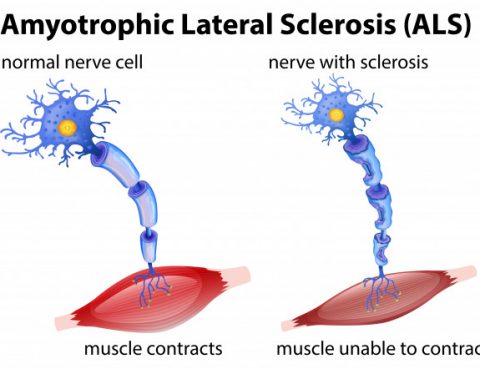
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or ALS is a progressive nervous system disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, causing loss of muscle control. ALS is often called Lou Gehrig’s disease, after the baseball player who was diagnosed with it. ALS and Motor Neurons It’s a disease that affects the motor neurons. These…

Rosacea is a common skin condition that causes redness and visible blood vessels in a person’s face. It may also produce small, red, pus-filled bumps. These signs and symptoms may flare up for weeks to months and then go away for a while. Rosacea can be mistaken for acne, other skin problems or natural ruddiness….
